ADENOIDITIS (ADENOIDS)
Inflammation of adenoids and their expansion are accompanied with chronic runny nose and is called adenoiditis, which is commonly seen in children. Adenoiditis symptoms include blocked nose, snoring in kids, ear problems, etc. Adenoiditis treatment aims to eradicate the infection and prevent its` recurrence, which in some cases means the need to perform a surgery (adenoidectomy). Below we are going to provide more detailed information about this condition.
Adenoids are two small patches of lymphatic tissue that sit in the back of the nasal cavity. They are also known as a pharyngeal tonsils or nasopharyngeal tonsils. Same as tonsils in your throat, adenoids help keep your body healthy by trapping harmful bacteria and viruses that you breathe in or swallow. They do important work as infection fighters for babies and toddlers. But they become less important once a child gets older and the body develops other ways to fight germs.
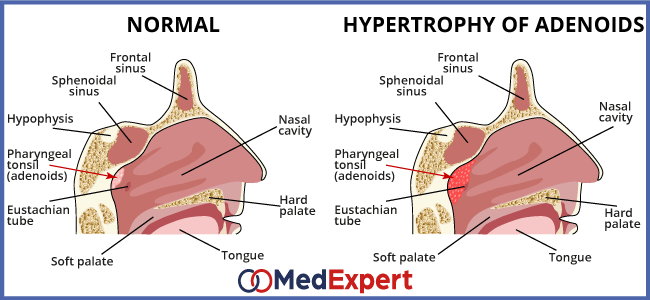
Sometimes, when overwhelmed with bacteria or viruses, adenoids may get swollen or enlarged causing discomfort.
ARE SWOLLEN ADENOIDS A SERIOUS CONDITION?
Swollen or enlarged adenoids can lead to severe distress in some children which can affect their daily life. Adenoidectomy is suggested by the doctor when children experience:
- Breathing problems: shortness of breath or breathing through the mouth.
- Difficulty sleeping: leading to heavy snoring or sleep apnea.
- Recurrent problems with the ear: as a result of middle ear infections or glue ear
- Recurrent or chronic sinusitis: exhibiting symptoms such as facial pain, nasal sounding speech or constant runny nose.
ADENOIDITIS SYMPTOMS
The following symptoms are as a result of swollen adenoids:
- Ear problems
- Blocked stuffy nose
- Difficulty sleeping
- Snoring
- Sore throat
- Swollen neck glands
- Difficulty breathing through the nose
- Glue ear
- Sleep apnea
- Dry mouth and cracked lips
ADENOIDITIS TREATMENT OPTIONS
- Medication: The use of antibiotics is often used for medication in the treatment of swollen adenoids.
- Adenoidectomy: In the event antibiotics do not work, surgery is carried out. Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed by a doctor who specializes in ear, nose and throat surgery. This process involves the removal of the adenoids through the mouth and is carried out under general anaesthesia.
RECOVERY FROM ADENOIDECTOMY
In the event after the completion of the surgery the following may be experienced or noticed in the child:
- Sore throat: This may occur in the child where eating would be difficult for about 10 days.
- Fever: A low-grade fever may develop in the child days after the surgery. It is advisable to seek medical attention if the fever rises beyond 102F and is accompanied by lethargy, nausea, headache or stiffness in the neck.
- Mouth Breathing: Due to the swelling of the throat, breathing through the mouth and snoring may occur in the child. This problem diminishes after 10 to 14 days.
- Pain: Throat and ear pan is expected in the child and can be dealt with through medication prescribed by the doctor.
- Scabs in the mouth: Thick white scabs may develop in the child where the adenoids were removed which can lead to bad breath. The scabs fall off on their own within 10 days.
HOW TO SPEED UP RECOVERY IN THE CHILD FOLLOWING AN ADENOIDECTOMY?
- Soft foods such as scrambled eggs, soup, jelly and popsicles should be prepared for the child following surgery.
- The child should not be allowed to take an dairy product in the first 24 hours after the surgery after which ice cream, pudding and yoghurt are fine.
- Abundant fluids should be taken to prevent dehydration.
- The child should have enough rest as possible the first few days after the surgery.
ADENOIDECTOMY: THE WARNING SIGNS
Medical attention should be sought immediately noticing the following signs in a child:
- Blood coming out of child’s mouth or nose (this maybe a sign of the scabs coming off too soon).
- Tiny spots of blood in the nose or saliva.
- Difficulty breathing or when wheezing starts (sigh that there is excessive swelling in the area surgery was performed).

DIAGNOSING ADENOIDITIS (ADENOIDS)
- Physical examination: Before performing an exam, questions about the symptoms in the child are asked.
- Nasal endoscopy: Nasoendoscopy is a minimally invasive, medical procedure carried out to diagnose any nasal conditions. It helps to examine the interior surfaces of the nose and allows visualization of its cavities not possible by standard examination. The procedure is performed with the help of a nasal endoscope which is a medical device consisting of a thin, rigid tube with fiberoptic cables to light-up the inside of the nose. The endoscope is then connected to a light source and a video camera to project magnified images on a screen. During the procedure your doctor may capture or record the images for further documentation.
- Throat examination: The doctor makes use of swabs to obtain samples of bacteria or viruses in the child’s throat.
- Blood tests: This is done to determine the presence of organisms.
- Head and neck x-ray: This is done to determine the size of the adenoids and the severity of the condition.


