Hypertensive Heart Disease
High blood pressure, which remains uncontrolled for a long time can cause a wide range of cardiac problems. As the heart muscle pumps blood against this pressure, it must work harder. This causes the heart muscle to thicken gradually, which results in hypertensive heart disease development over time. The range of hypertensive heart disease treatment options include conservative methods and surgical procedures, such as implantation of cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) and coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). Below we will discuss in detail symptoms and treatment option for hypertensive heart disease, as well as diagnostic procedures to discover the disease.
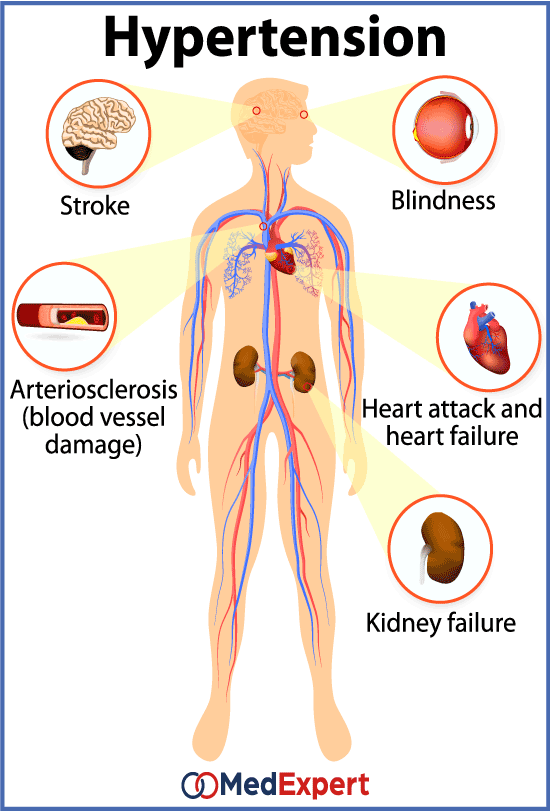
Hypertensive heart disease refers to heart conditions that are caused by high blood pressure over a long period of time. This occurs when the pressure inside the blood vessels (arteries) is too high. As the heart must work harder to pump against this pressure, the heart muscle thickens over time. There are a number of heart disorders that are caused by the heart working under increased pressure.
Common heart conditions caused by Hypertensive heart disease:
- Heart failure
- Thickening of the heart muscle
- Coronary artery disease
A variety of changes in the myocardial structure, coronary vasculature, and conduction system of the heart can occur due to uncontrolled and prolonged elevation in blood pressure.
Over time, these changes can lead to the development of:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Various conduction system diseases
- Systolic and diastolic dysfunction of the myocardium
- Angina or myocardial infarction
- Cardiac arrhythmias (especially atrial fibrillation)
- Congestive heart failure (CHF)
Hypertensive heart disease may cause serious health problems and it is the leading cause of death from high blood pressure.
SYMPTOMS OF HYPERTENSIVE HEART DISEASE
Depending on the severity of the condition and progression of the disease, the symptoms may vary. You may experience no symptoms. If you do experience symptoms, they may include:
- Pain in chest (angina)
- Tightness or pressure in the chest
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Pain in neck, back, arms, or shoulders
- Persistent cough
- Loss of appetite
- Swelling (foot or ankle)
HYPERTENSIVE HEART DISEASE TREATMENT OPTIONS
The treatment method used will depend on the seriousness of your illness, your age, and your medical history. Treatments may include:
Medication
Prescribed drugs can help your heart in various ways. They can help to prevent your blood from clotting, improve the flow of your blood, and lower your cholesterol. It is important to always follow instructions given by your doctor. Examples of common medications for heart disease include:
- Water pills: To help lower blood pressure
- Nitrates: To treat chest pain
- Statins: To treat high cholesterol
- Beta-blockers: To lower blood pressure and reduce the amount of oxygen used by the heart
- Aspirin: To prevent blood clots
Surgeries and Devices
In extreme cases, surgery may be needed to increase blood flow to your heart. Your doctor may surgically implant a battery-operated device called a pacemaker in your chest or abdomen if you need assistance in regulating your heart’s rate or rhythm.
A pacemaker works to produce electrical stimulation that will cause cardiac muscle to contract. The implantation of a pacemaker is crucial and beneficial when cardiac muscle electrical activity is abnormally slow or absent.
- Cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs): Implantable devices used to treat serious, life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias.
- Coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG): Treats blocked coronary arteries. This is only performed for severe coronary heart disease.
If your condition is especially severe, a heart transplant or other heart-assisting devices may be necessary.
DIAGNOSING HYPERTENSIVE HEART DISEASE
-
- History taking and physical exam: Your doctor will ask you questions about your usual life style, symptoms you are having and family history of heart diseases. Then he will perform a physical examination, which includes checking you pulse, blood pressure, auscultation and percussion of your heart. Your doctor will search for certain signs of hypertensive heart disease, including:
- High blood pressure
- Enlarged heart
- Irregular heartbeat
- Fluid in the lungs or lower extremities
- Unusual heart sounds
- History taking and physical exam: Your doctor will ask you questions about your usual life style, symptoms you are having and family history of heart diseases. Then he will perform a physical examination, which includes checking you pulse, blood pressure, auscultation and percussion of your heart. Your doctor will search for certain signs of hypertensive heart disease, including:
One or more of the following tests may be performed to help determine the cause of your symptoms:
- Electrocardiogram: Patches attached to your chest, legs, and arms will be used to monitor and record your heart’s electrical activity. Results will be visible on a screen and your doctor will interpret them.
- Echocardiogram: A detailed picture of your heart will be taken using an ultrasound.
- Coronary angiography: This test examines the flow of blood through your heart. A catheter is inserted through your groin or an artery in your arm and up into the heart.
- Exercise stress test: Examines how exercise affects your heart. Your doctor may ask you to pedal an exercise bike or walk on a treadmill.
- Nuclear stress test: This test examines the flow of blood into the heart. It is usually conducted while you’re resting and exercising.


